Kim Huynh, Guohong Wang, Warren Rodrigues, Rehka Barhate, Cynthia Coulter, Michael Vincent, James Soares Immunalysis Corporation, Pomona, CA USA
Abstract
Fentanyl is an extremely potent synthetic opioid widely used in the treatment of chronic pain. It is available as patches, tablets and injectable solutions. It is highly addictive and prone to abuse.
A high throughput homogeneous enzyme immunoassay (HEIA) has been developed for the detection of fentanyl in human urine. An antibody capable of measuring fentanyl at low concentrations was used. The initial evaluation used human urine samples that had been previously confirmed positive or negative for fentanyl/norfentanyl by LC-MS/MS.
Objectives
- To develop a high throughput homogeneous enzyme immunoassay (HEIA) for the detection of fentanyl in urine.
- To ensure the agreement between immunoassay and LC-MS/MS is >95%.
- To ensure minimal interference from commonly used drugs.
Methods
The HEIA uses a fentanyl antibody and fentanyl labeled enzyme (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH). The assay is based on the competition between fentanyl labeled G6PDH and the free drug in a urine sample for the fixed amount of antibody binding sites. In the absence of free drug, the antibody binds the drug enzyme conjugate and enzyme activity is inhibited. Free drug in urine reverses the inhibition. This creates a dose response relationship between drug concentration in the urine and enzyme activity. The enzyme G6PDH activity is determined at 340nm spectrophotometrically by the conversion of NAD to NADH.
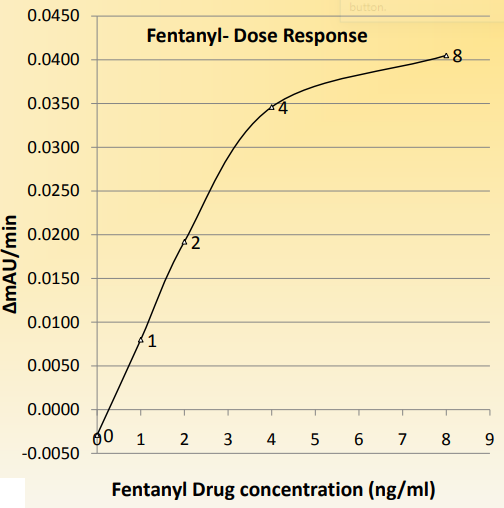
Results and Discussion
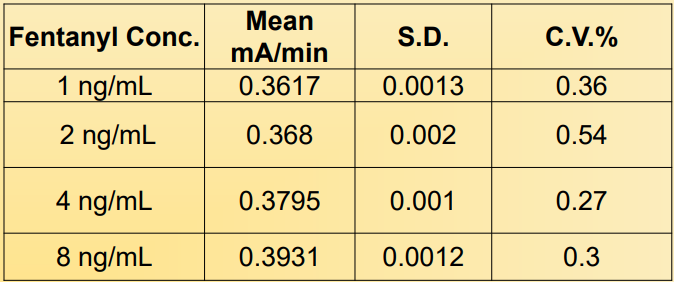
Intra-assay Precision:
Precision was determined by assaying calibrators and controls using 10 replicates.
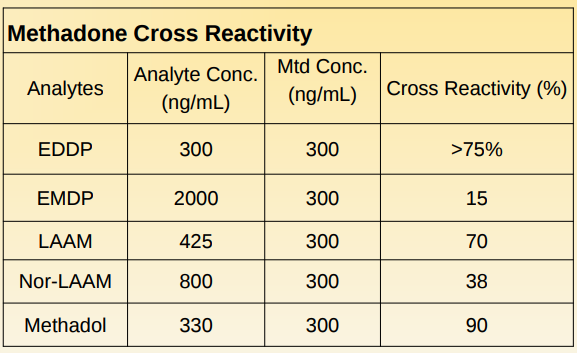
Cross Reactivity:
Two related compounds (norfentanyl and despropionylfentanyl) were added to synthetic urine and their cross reactivity appears in the table below. Based on our knowledge of the immunogen, we would expect 3-OH- fentanyl and similar metabolites to show significant cross reactivity. However, these compounds were not available for testing.
Authentic Specimens:
117 urine specimens were obtained from a commercial laboratory. The specimens were a combination of positive and negative urines, and were analyzed by HEIA and LC-MS/MS using cutoffs of 2 and 1 ng/mL respectively. 39 specimens were negative by both methods; 75 were positive by both methods. The sensitive, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value were calculated to be 100%, 93%, and 100% respectively.

Three urine specimens that were positive at a screening cutoff of 2 ng/mL did not confirm positive at a confirmatory cutoff of 1 ng/mL for fentanyl.
Summary
A high throughput HEIA for fentanyl in human urine has been developed. The positive/negative predictive values as determined by HEIA correlate well with LC-MS/MS.
References
- R.C. Baselt and R.H. Cravey. Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man, 8th edition. 616-619
SOFT, Oklahoma City, 2009
To view the full study and its data, visit this link.
Looking for equipment or accessories for your immunoassay and other related applications?? Check out our products below.
- Block Scientific Chemistry and Immunoassay Analyzers
- Immunalysis Calibrators
- Immunalysis Controls
- Immunalysis Reagents


